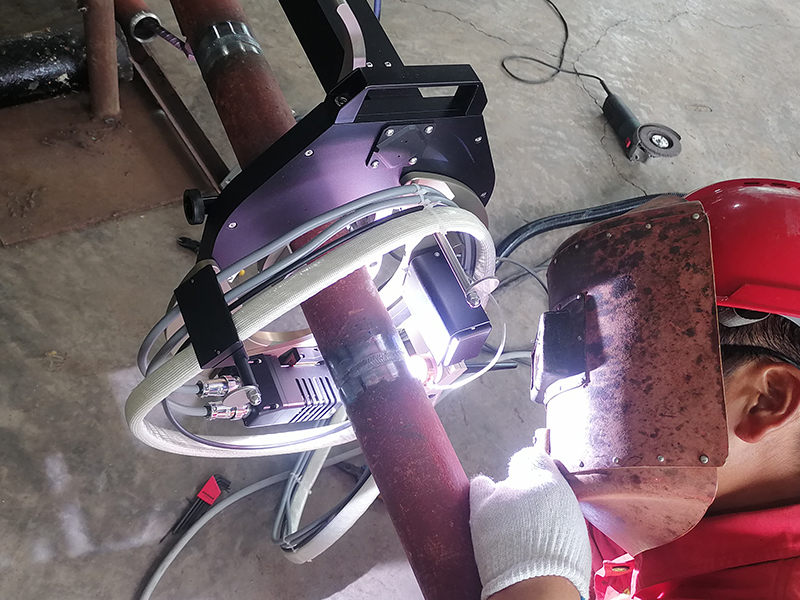
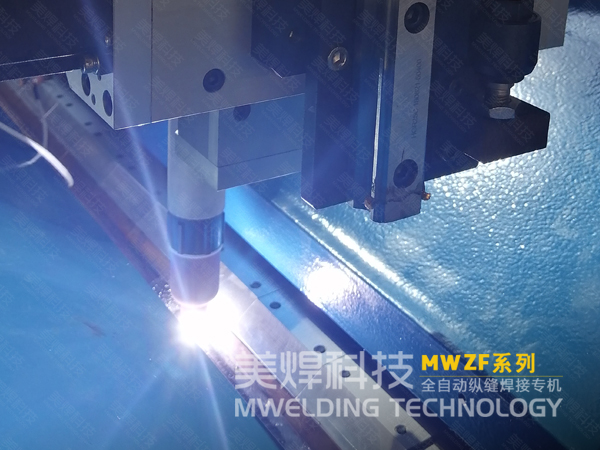
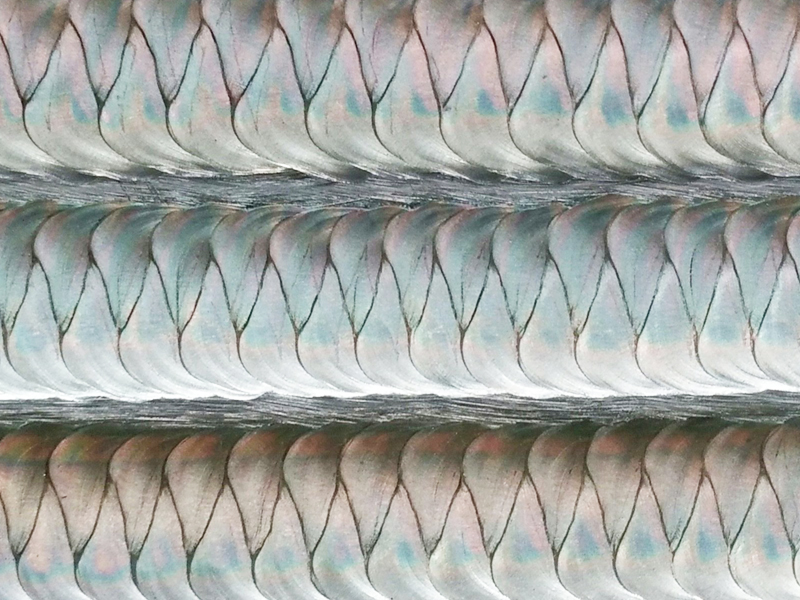
TIG welding is a high - quality welding method. If you want to create beautiful fish - scale weld patterns, here are the detailed key points and precautions during the TIG welding process:
Arc - starting
There are two arc - starting methods in TIG welding: contact arc - starting and non - contact arc - starting. Non - contact arc - starting generates a high - frequency and high - voltage electric field between the tungsten electrode and the workpiece through a high - frequency oscillator or a high - voltage pulse generator, ionizing the gas to start the arc. This method can effectively prevent tungsten electrode contamination and is widely used in precision welding. When starting the arc, it should be done on the arc - starting plate of the workpiece, avoiding starting the arc at the formal weld position of the workpiece to prevent defects.
Welding Parameter Control
Welding current is one of the key parameters. If the current is too large, the weld pool will be too deep, the weld will be too wide, and defects such as burn - through and undercut are likely to occur. If the current is too small, the temperature of the weld pool will be insufficient, the weld will not be well - fused, and problems such as lack of penetration may appear. For example, when welding 3mm - thick aluminum alloy, the welding current is generally controlled between 80 - 120A.
The welding speed should also be appropriate. If the welding speed is too fast, the reinforcement of the weld will be too low, the weld width will be narrow, and even lack of fusion may occur. If the welding speed is too slow, too much molten pool metal will accumulate, the weld will be too high, and overheating may also occur. For welding a 10mm - thick carbon steel pipeline, a welding speed of generally 8 - 12cm/min is more appropriate.
The argon gas flow rate should be kept stable. If the argon gas flow rate is insufficient, air will invade the weld pool, causing defects such as pores and oxidation in the weld. If the argon gas flow rate is too large, it will cause waste of argon gas and may lead to turbulence in the welding area, affecting the gas protection effect. When welding in a windy environment, it is necessary to appropriately increase the argon gas flow rate or take wind - proof measures.
Wire - feeding Method
For manual TIG welding, the wire - feeding methods include continuous wire - feeding and intermittent wire - feeding. When continuously feeding the wire, the wire - feeding speed should match the welding speed to ensure that the wire can be evenly melted into the weld pool. Intermittent wire - feeding is often used for welds with small gaps. When the molten pool metal is about to solidify, the wire is quickly fed into the weld pool and then withdrawn, repeating this operation. The wire - feeding position should be accurate, generally at the front of the weld pool, so that the wire can be fully mixed with the molten pool metal.
Welding Posture and Position
The welder's posture should be comfortable and stable to enable flexible operation of the welding torch and wire - feeding. When welding in the flat welding position, the angle between the welding torch and the workpiece surface is generally 70° - 80°, and the angle between the wire and the workpiece surface is 10° - 15°. In the vertical welding position, the upward vertical welding or downward vertical welding method can be adopted. When using upward vertical welding, the welding torch angle is 60° - 70°, and when using downward vertical welding, the welding torch angle is 80° - 90°. Also, the size of the weld pool should be controlled to prevent the molten pool metal from flowing down.
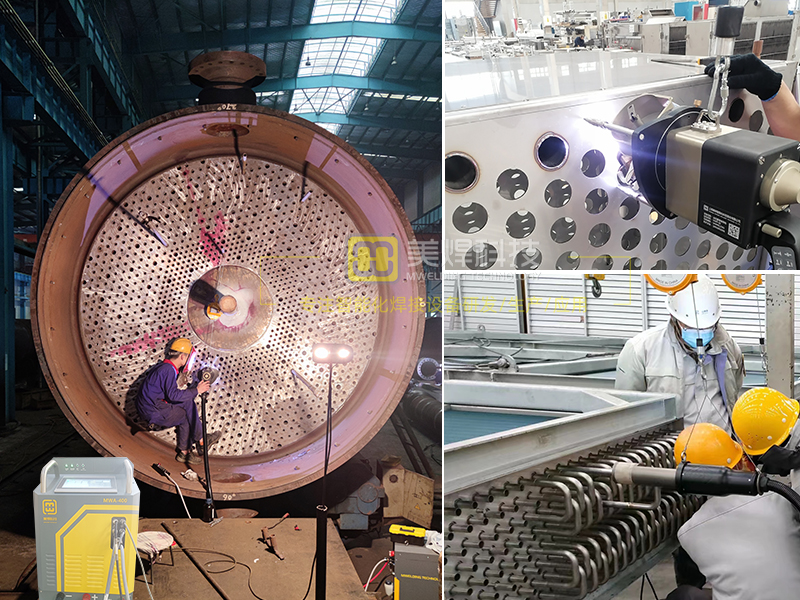
It would be great if there was a device that could start welding directly just by inputting the welding pipe diameter and wall thickness. In actual production, the appropriate welding process should be selected according to factors such as the material, thickness, and shape of the pipe fittings to ensure welding quality and efficiency. Strict quality control and testing should be carried out to ensure the reliability of the welded joints. The Mwelding Pipe - to - Pipe Automatic Welder, as an excellent portable pipeline welding device, is widely used in related manufacturing and processing fields.
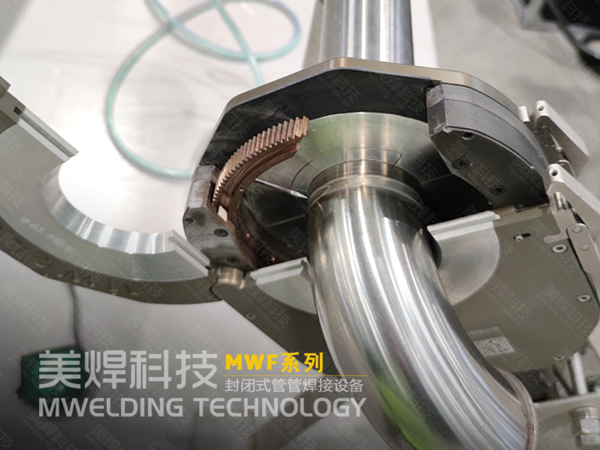

Features of this Portable Pipe - to - Pipe Automatic Welder
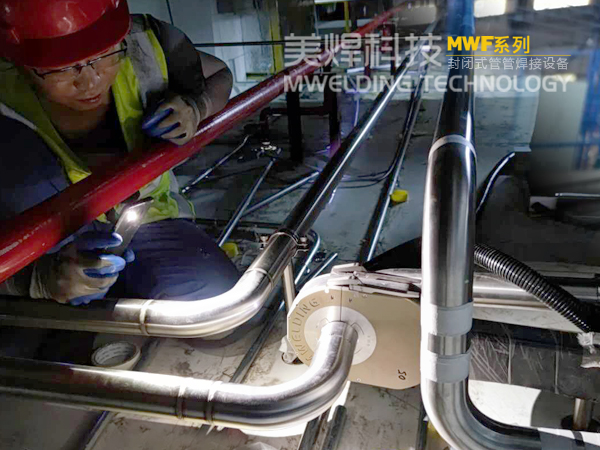
This kind of portable pipe - to - pipe automatic welder adopts a closed - type head design, which can well ensure sufficient argon gas protection for the weld during the welding process and reduce the influence of external environmental factors such as wind.
The device uses a tungsten - needle orbital precise - surrounding structure to ensure that the welding distance between the tungsten needle and the pipe fittings remains constant during the welding process. Compared with traditional manual operations, the arc voltage is more stable, and the forming is uniform.
The digital intelligent welding control system can accurately set and adjust parameters such as welding current, voltage, and welding speed, effectively controlling the heat input during welding. This can better control the heat - affected zone of the welding, improve welding quality, reduce weld defects, and ensure the service performance of the welded pipe fittings.
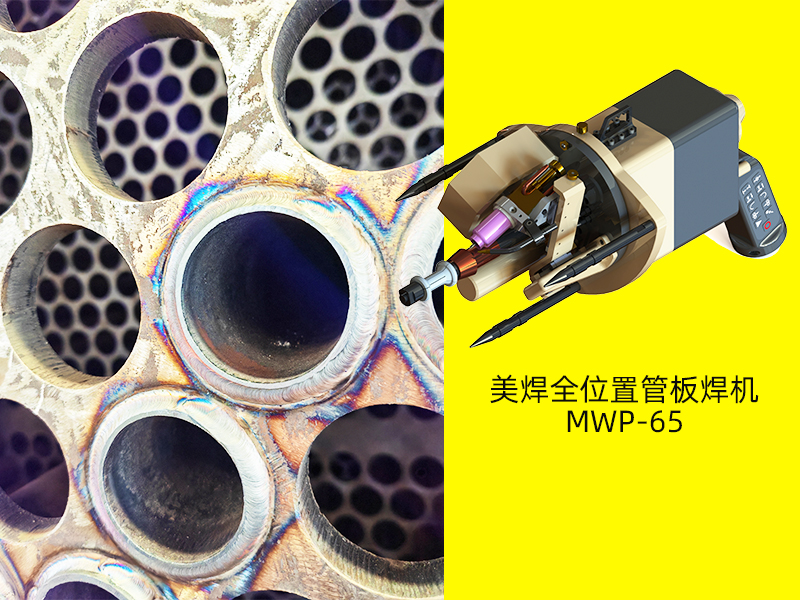
The ultra - thin, compact or mini - clamping welder structure has good accessibility in narrow and high - altitude working spaces where manual operation is difficult. The precise mini - clamping and welding mechanism helps to improve the welding quality and efficiency of small - diameter pipe fittings.
The device does not require professional welding skills, and even novices can weld high - quality welds in minutes. The expert welding parameter support equipped in the system effectively ensures professional welding performance.
The digital intelligent management mode of the welding program can greatly reduce the dependence on welding skills. With the precise control of the device, standardized welding operation management can be achieved, making large - scale, high - standard and uniform welding output possible. Production managers can obtain good economic benefits through reasonable equipment and personnel allocation and lean management.
MWF - 120 Pipe - to - Pipe Welder Demonstrates Welding Strength
In response to the continuously rising labor cost and management challenges, the MWF Pipe Automatic Welder, which anyone can operate after simple training, fundamentally solves the production problems. It turns the welding process, which is difficult for ordinary people to master, into an intelligent and digitally controllable standardized operation. While representing an advanced production method and high - efficiency processing ability, it changes the employment mode at the business bottom, making employment more flexible, and enabling rapid optimization and improvement of processing capabilities. This also makes enterprise production management easier.